Introduction
Imagine you’re at your favorite local coffee shop, eager to get your caffeine fix and start your day. As you approach the counter to pay, you notice the barista swiping your card through a small device attached to their tablet. Ever wonder how that transaction goes through, and who’s responsible for processing it?
This is where the world of payment processing comes into play, and it’s a complex industry with multiple players involved. Two important players in this space are merchant acquirers and payment processors. While these terms might seem interchangeable, they have distinct roles and functions in the payment processing ecosystem.
In this blog, we’ll dive into merchant acquirer vs payment processor, how they work together, and which one might be the right fit for your business. Understanding the nuances of these two players is crucial for anyone in the business of accepting payments, so whether you’re a small business owner or just a curious consumer, let’s get started!
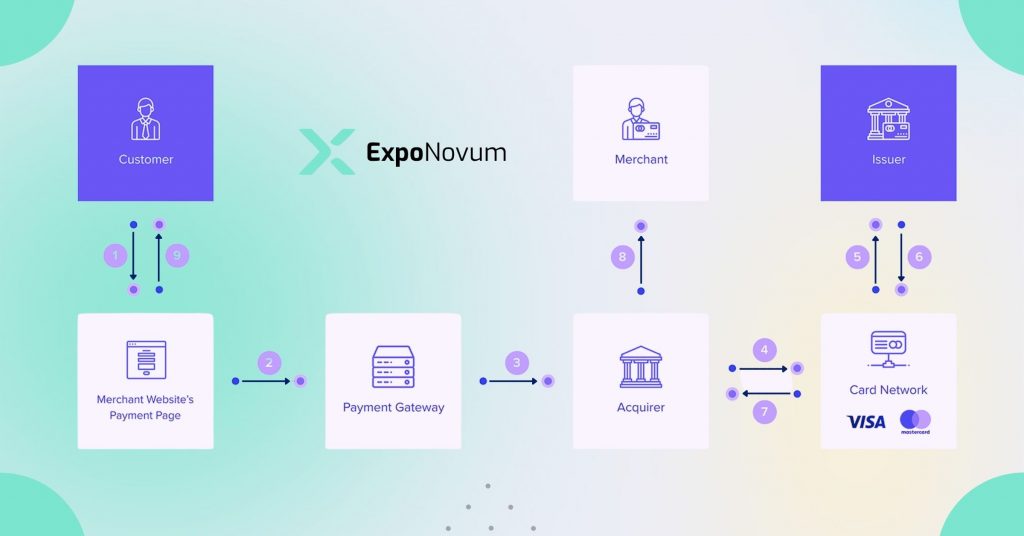
Merchant Acquirer
Merchant acquirers are an essential component of the payment processing system, and they play a crucial role in helping businesses accept card payments. In this chapter, we’ll explore what merchant acquirers are, their role in payment processing, and some examples of popular merchant acquirers.
Definition of Merchant Acquirer
- Merchant acquirers are financial institutions that work with businesses to enable them to accept card payments from their customers.
- They act as an intermediary between the business and the issuing bank that provides the customer’s card.
Role of Merchant Acquirer in Payment Processing
- Merchant acquirers are responsible for setting up and maintaining the payment processing infrastructure that businesses use to accept card payments.
- They work with payment processors to route transactions to the appropriate issuing bank, authorize transactions, and settle funds to the business’s account.
- They also provide support and customer service to businesses regarding their payment processing needs.
Examples of Popular Merchant Acquirers
- Some popular merchant acquirers include Chase Paymentech, First Data, Elavon, and Global Payments.
- Each of these acquirers has its strengths and weaknesses, and businesses should carefully evaluate their options before choosing a merchant acquirer to work with.
Overall, merchant acquirers are a critical piece of the payment processing puzzle, and businesses need to choose the right partner to ensure they can accept card payments reliably and efficiently. In the next chapter, we’ll explore payment processors and how they differ from merchant acquirers.
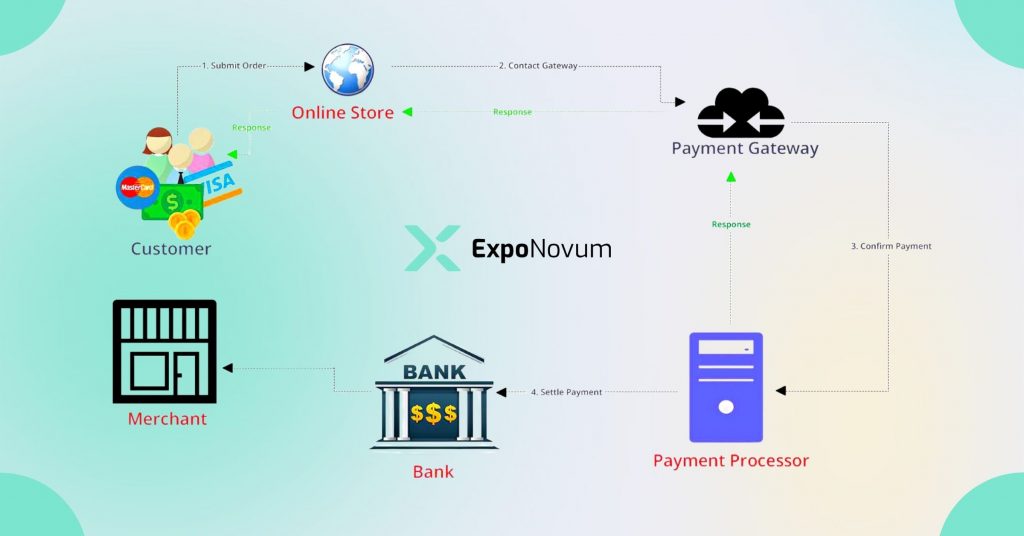
Payment Processor
Payment processors are another critical player in the payment processing ecosystem. In this chapter, we’ll explore what payment processors are, their role in payment processing, and some examples of popular payment processors.
Definition of Payment Processor
Payment processors are companies that facilitate the electronic transfer of funds between buyers and sellers. They work with merchant acquirers to process transactions on behalf of businesses that accept card payments.
Role of Payment Processor in Payment Processing
- Payment processors are responsible for handling the actual processing of card payments.
- They receive transaction data from the merchant acquirer, communicate with the issuing bank to authorize the transaction, and then settle funds to the merchant’s account.
- They also provide support and customer service to businesses regarding their payment processing needs.
Examples of Popular Payment Processors
- Some popular payment processors include PayPal, Stripe, Square, and Authorize.Net.
- Each of these payment processors has its strengths and weaknesses, and businesses should carefully evaluate their options before choosing a payment processor to work with.
Overall, payment processors are a crucial part of the payment processing system and work closely with merchant acquirers to ensure that businesses can accept card payments efficiently and securely. In the next chapter, we’ll dive into the differences between merchant acquirers and payment processors and how they work together in the payment processing ecosystem.
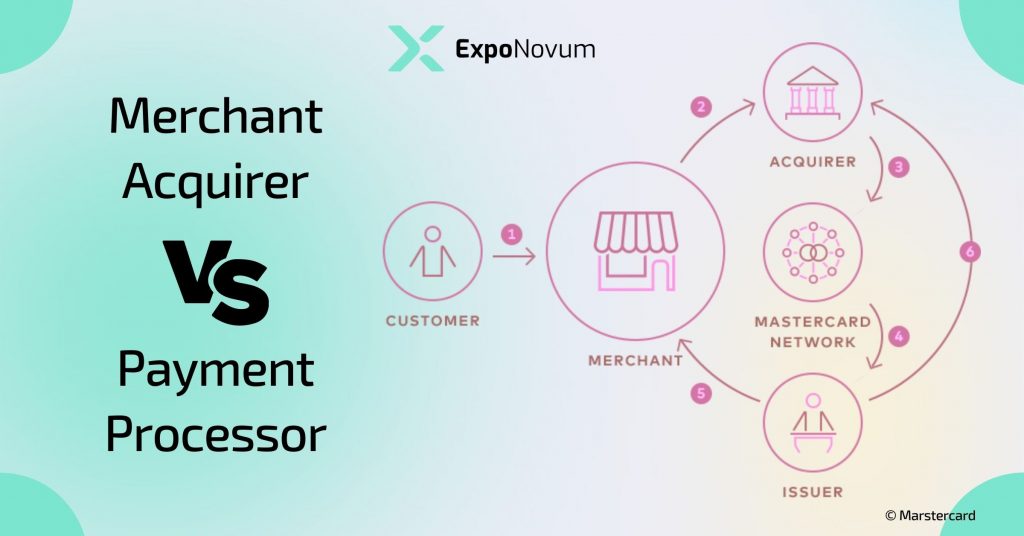
Merchant Acquirer vs Payment Processor
Payment processing is a complex system that involves several players, including merchant acquirers and payment processors. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they are distinct entities with different roles and responsibilities. In this article, we will explore the key differences between merchant acquirers and payment processors.
Definition and Roles
Merchant acquirers are financial institutions that work with businesses to enable them to accept card payments. They typically provide businesses with point-of-sale (POS) terminals, card readers, and other hardware and software needed to process payments. Merchant acquirers also manage the communication and exchange of payment information between the business, the card issuer, and the payment processor.
Payment processors, on the other hand, are companies that handle the actual processing of card payments. They work with both merchant acquirers and card networks, such as Visa and Mastercard, to facilitate transactions between businesses and consumers. Payment processors are responsible for verifying the transaction details, authorizing the payment, and transferring funds between the card issuer and the business.
Ownership and Control
Merchant acquirers typically own the relationship with the business and have control over the transaction process. They are responsible for managing the risk associated with the business and ensuring compliance with payment industry regulations. Payment processors, on the other hand, are third-party entities that are responsible for processing payments on behalf of the merchant acquirer and the card network.
Fees and Pricing
Merchant acquirers typically charge businesses a fee for each transaction processed, which can include a variety of fees such as interchange fees, processing fees, and monthly fees. Payment processors also charge fees for their services, including per-transaction fees and percentage-based fees on the total transaction amount. These fees are typically shared between the merchant acquirer and the payment processor.
Security and Fraud Prevention
Both merchant acquirers and payment processors are responsible for ensuring the security of payment transactions and preventing fraud. Merchant acquirers are responsible for conducting due diligence on businesses to mitigate the risk of fraud and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Payment processors use advanced fraud detection tools and technologies to prevent fraudulent transactions.
Customer Support and Service
Merchant acquirers typically provide customer support and service to businesses, including technical support for hardware and software issues, as well as assistance with payment disputes and chargebacks. Payment processors may also provide customer support, but their primary focus is on processing payments.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding the differences between merchant acquirers and payment processors is crucial for any business owner who wants to accept electronic payments. By knowing the roles that each of these providers plays in the payment processing ecosystem, you can make informed decisions that will help you save money and improve your customers’ experience.
When it comes to choosing the right provider for your business, remember to consider factors such as fees, security, payment methods, customer support, integration, and reputation. By keeping these factors in mind and doing your research, you can find a provider that meets your needs and helps you grow your business.
So don’t wait any longer – start exploring your options today and choose a provider that can help you take your business to the next level!